How many diabetes risk factors do you have?
- Genetic variation
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Obesity and fat accumulation (around the abdomen)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Prediabetes – elevated blood sugar
- Gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Understand your genetic risk of type 2 diabetes and make changes today to improve your metabolic health
Diabetes is one of the fastest growing diseases in the 21st century, affecting 422 million people worldwide. Type 2 diabetes is generally associated with an unhealthy lifestyle and extra body weight, but genetic variations can also increase your risk, regardless of your lifestyle. Knowledge of genetic variants that increase your risk of type 2 diabetes allows you to make lifestyle changes today to improve your metabolic health and reduce your risk of this debilitating condition.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that disrupts the body’s normal glucose and insulin balance. Glucose is a simple sugar that circulates in the blood and is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, while insulin is a hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas and helps to keep glucose levels within a healthy range. Affected individuals have consistently high blood sugar, insulin resistance and a relative lack of insulin. Type 2 diabetes can contribute to life-threatening disorders, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure and poor blood flow.
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes
- Genetic variation
- Obesity, leading to insulin resistance
- Fat accumulation, primarily in the abdomen
- Lack of physical exercise
- Ethnicity (Africans and American Indians have a higher risk)
- Prediabetes (elevated blood sugar)
- Gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Genetics of type 2 diabetes
Genetic variations can affect our glucose and insulin levels, sensitivity to dietary fatty acids, and the way our body responds to insulin, resulting in increased risk of type 2 diabetes. The following table lists the genes analyzed in the type 2 diabetes test, and the effect of variation on metabolic health.
| Gene(s) Tested | Effect |
| ACC2 | Reduced response to insulin |
| ADCY5 | Inhibited secretion of insulin |
| FABP2, FTO | Increased uptake of saturated fats |
| ADIPOQ, CRY2, FADS1, G6PC2, GLUT2, MTNR1B, PROX1, TCF7L2 | Increased fasting glucose levels |
| GCKR | Reduced fasting glucose levels |
| GCK, HNF4A | Reduced pancreatic beta cell function |
| GLIS3, IRS1, SLC30A8 | Disrupted insulin production/signalling/storage |
| SHBG | Increased sex hormone binding globulin |
| MADD | Impaired proinsulin-to-insulin conversion |
| SOD2 | Increased reactive oxygen species |
| HIF1A | Resistance to hypoxia |
Three Easy Steps
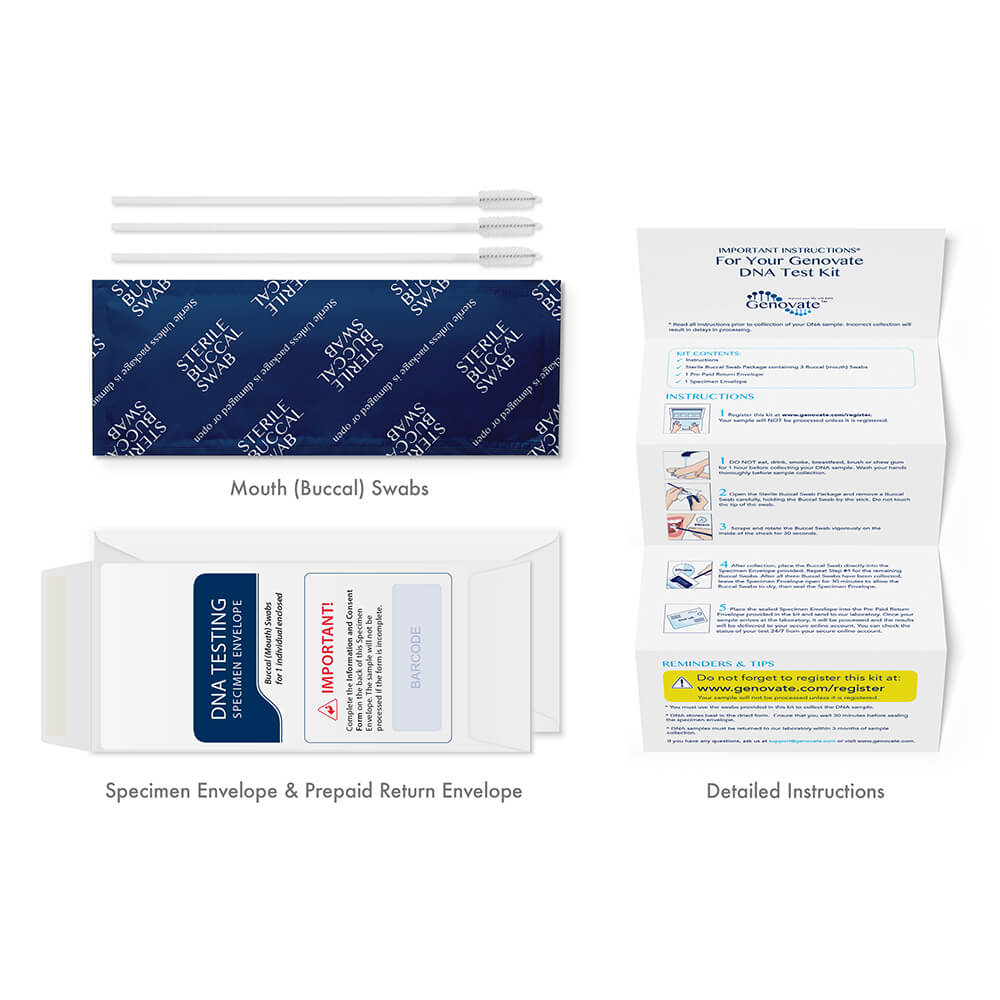
Step 1: Order test kit online
Step 2: Collect DNA sample using a painless mouth swab, and mail to the lab in the provided return envelope
Step 3: Receive your results online
Click here for more details and to watch our explanatory video.
| Benefits |
|---|
| ✓ Understand your genetic risk of type 2 diabetes |
| ✓ Make lifestyle changes today to improve your metabolic health |
| ✓ Painless buccal (mouth) swab sample collection |
| ✓ All tests are run 2x for absolute accuracy |
| ✓ Quickly collect samples in the privacy of your own home |
| ✓ 24/7 online test status check |
| ✓ Discreet online results option available |
| ✓ No age limit |
| ✓ State-of-the-art accredited testing laboratory |
Related products
Health & Disease
Find out if aspirin is the best treatment for you.
Health & Disease
Quickly determine your optimum warfarin dose.
Health & Disease
Understand your genetic risk of cardiovascular disease.
Health & Disease
Determine if you carry the genes linked to iron overload.
Health & Disease
Determine if your genes increase your risk of narcolepsy.
Health & Disease
Understand your risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease.
Health & Disease
Determine your genetic risk of osteoporosis.
Health & Disease
Determine whether you carry the APOE genetic variant linked to cardiovascular disease.